Michael Naguib, Olha Mashtalir, Joshua Carle, Volker Presser, Jun Lu, Lars Hultman, Yury Gogotsi, and Michel W. Barsoum, “Two-Dimensional Transition Metal Carbides”, ACS Nano, Vol 6, No. 2, 1322-1331, 2012
ACerS' Ross Coffin Purdy Award will recognize the article, which was the first to describe a facile method to produce a large family of two-dimensional layered, early transition metal carbides and nitrides, labeled MXenes. The latter are so-called because they are produced by selective etching of the A-group element — aluminum in this case — from an even larger family of layered solids labeled the MAX phases. The MAX phases were in turn discovered by Michel Barsoum, Ph.D., and co-workers roughly 15 years ago at Drexel University.
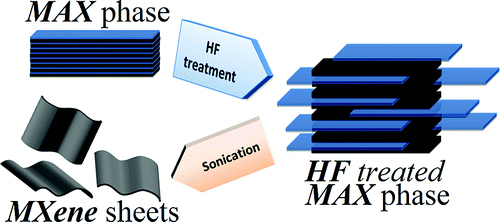
synthesis of two-dimensional transition metal carbides and carbonitrides by immersing select MAX phase powders in hydrofluoric acid
Barsoum, A.W. Grosvenor and Distinguished Professor at Drexel University, and Distinguished University Professor and Trustee Chair Yury Gogotsi, Ph.D., also from Drexel Materials, were co-authors of the award-winning paper, along with students Michael Naguib, Olha Mashtalir and Joshua Carle, together with collaborators from Linkoping University in Sweden.
The annual Ross Coffin Purdy Award recognizes researchers "judged to have made the most valuable contribution to ceramic technical literature." The ACerS board unanimously agreed to grant the honor to the Barsoum and Gogotsi team's work. The award will be presented in October during the Materials Science and Technology Conference in Montréal, Canada.
MXenes have potential uses in a broad range of energy and electronics applications, including lithium-ion batteries and supercapacitors. The materials' layered structure resembles that of graphene — hence the suffix ene — a two-dimensional sheet of carbon, but its chemistry is more complex and more versatile.
Read More about two dimensional transition metal carbides on mrc.org.ua